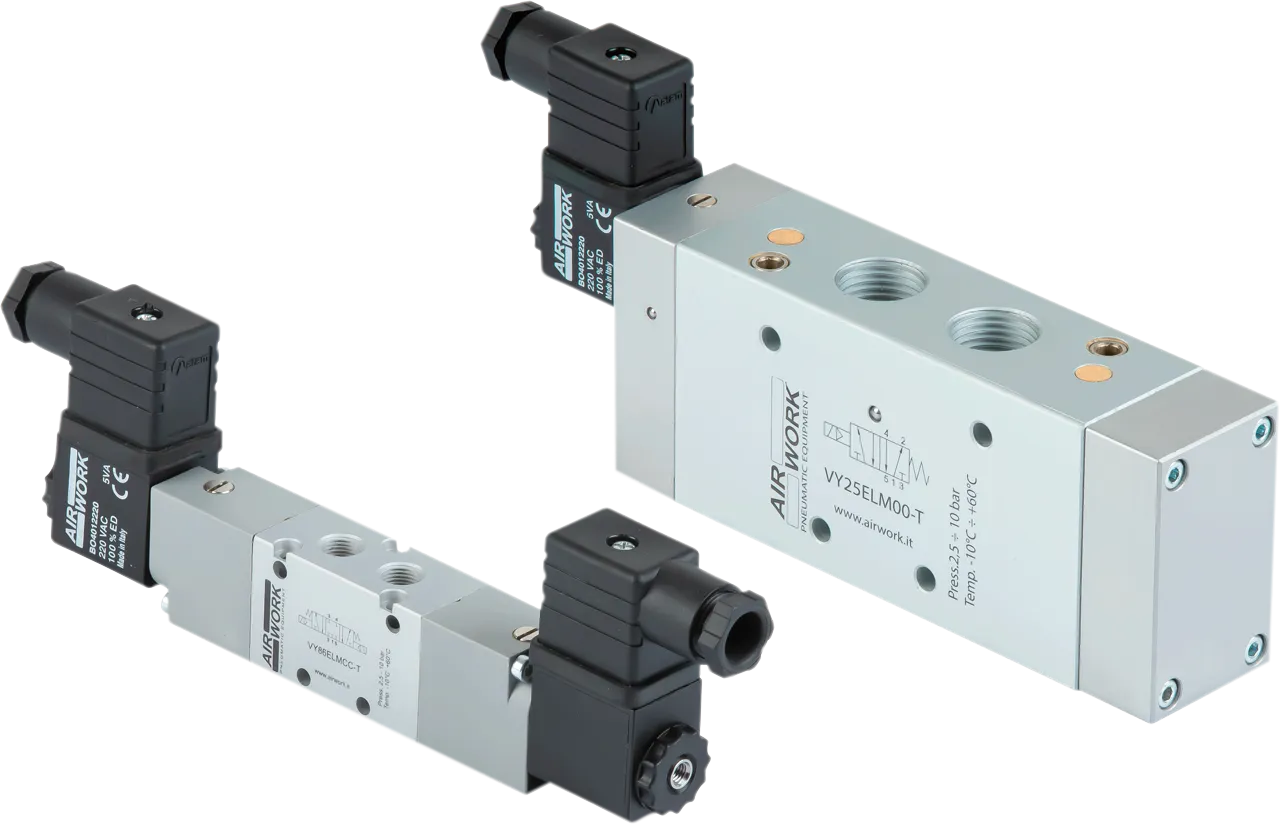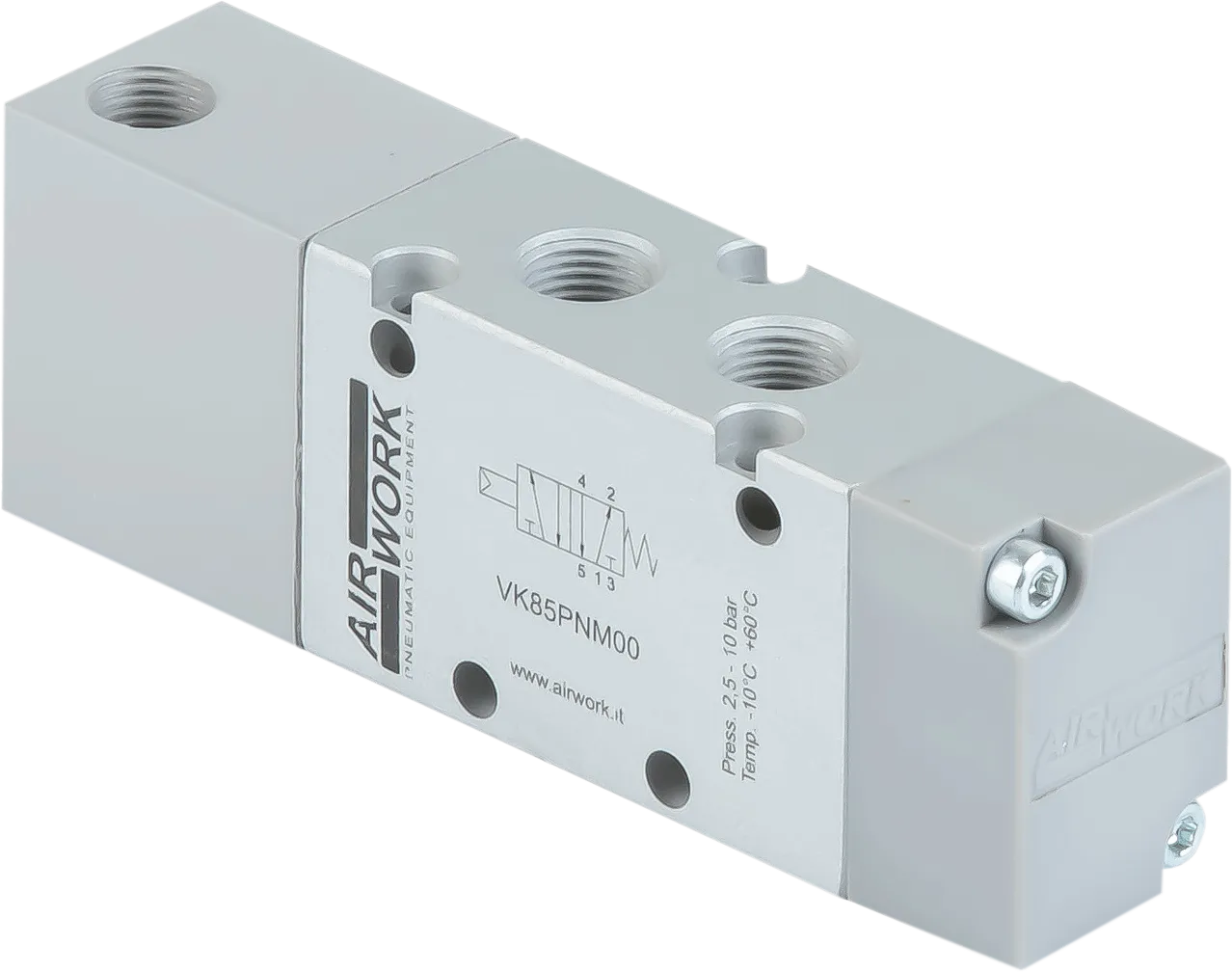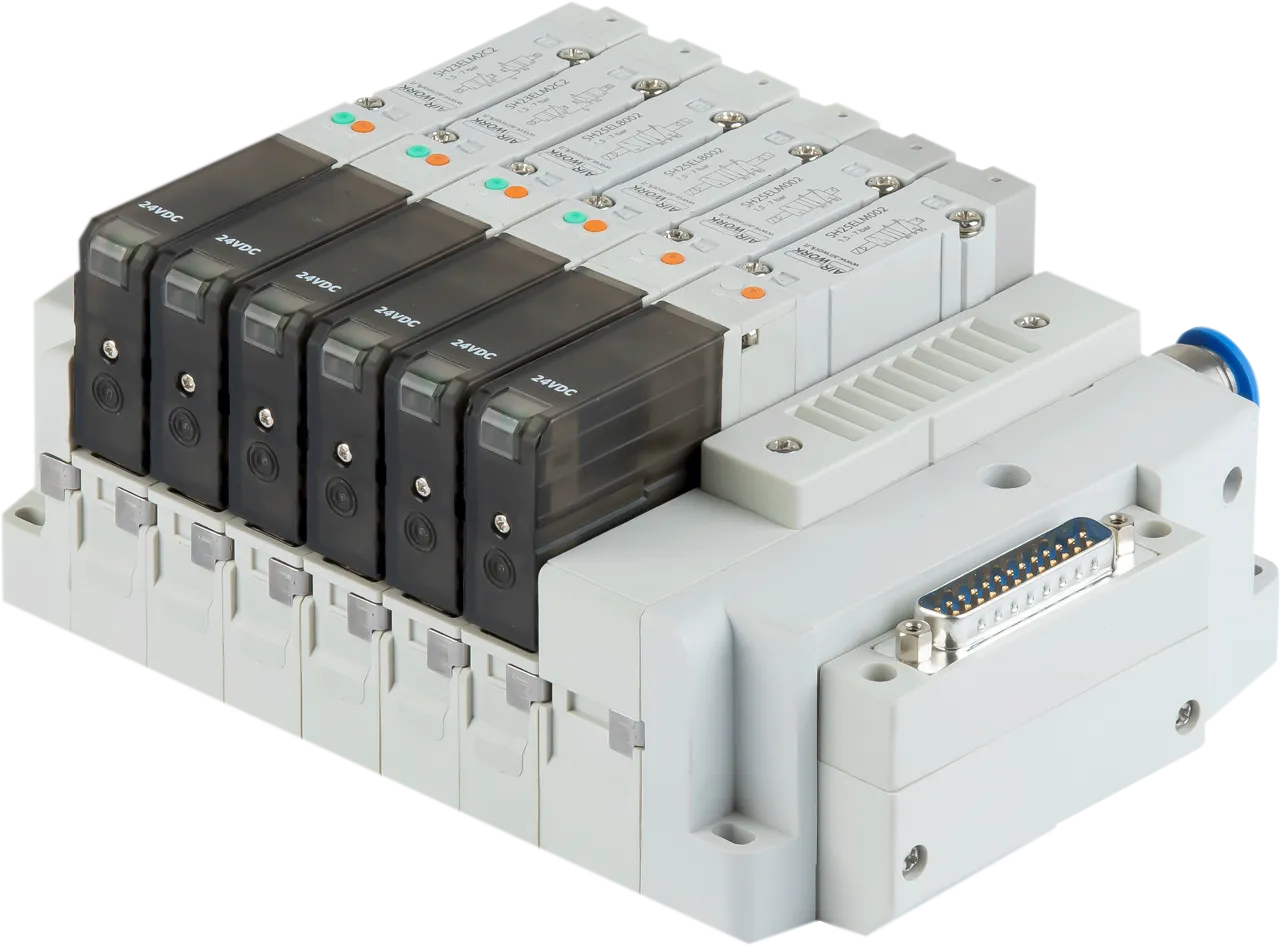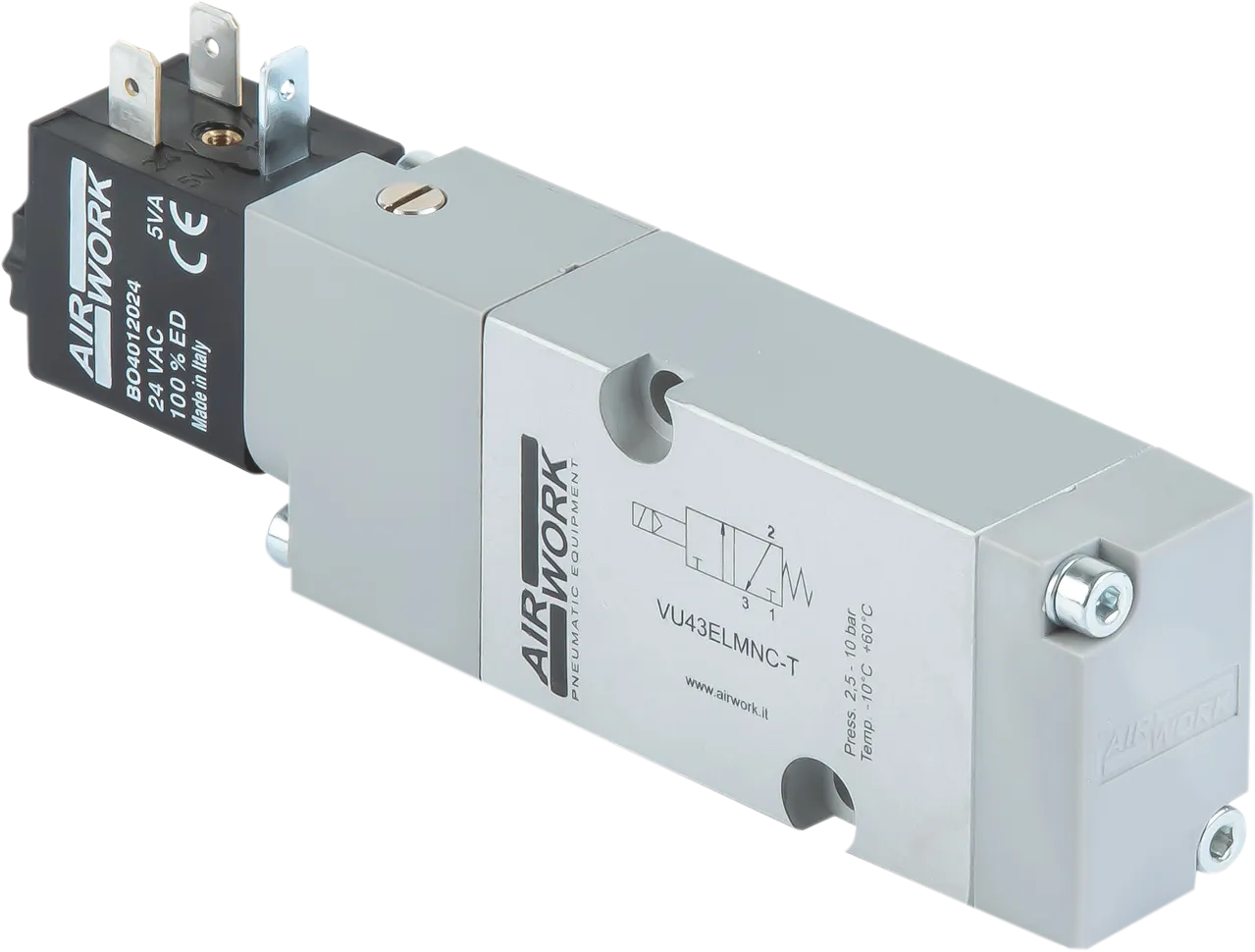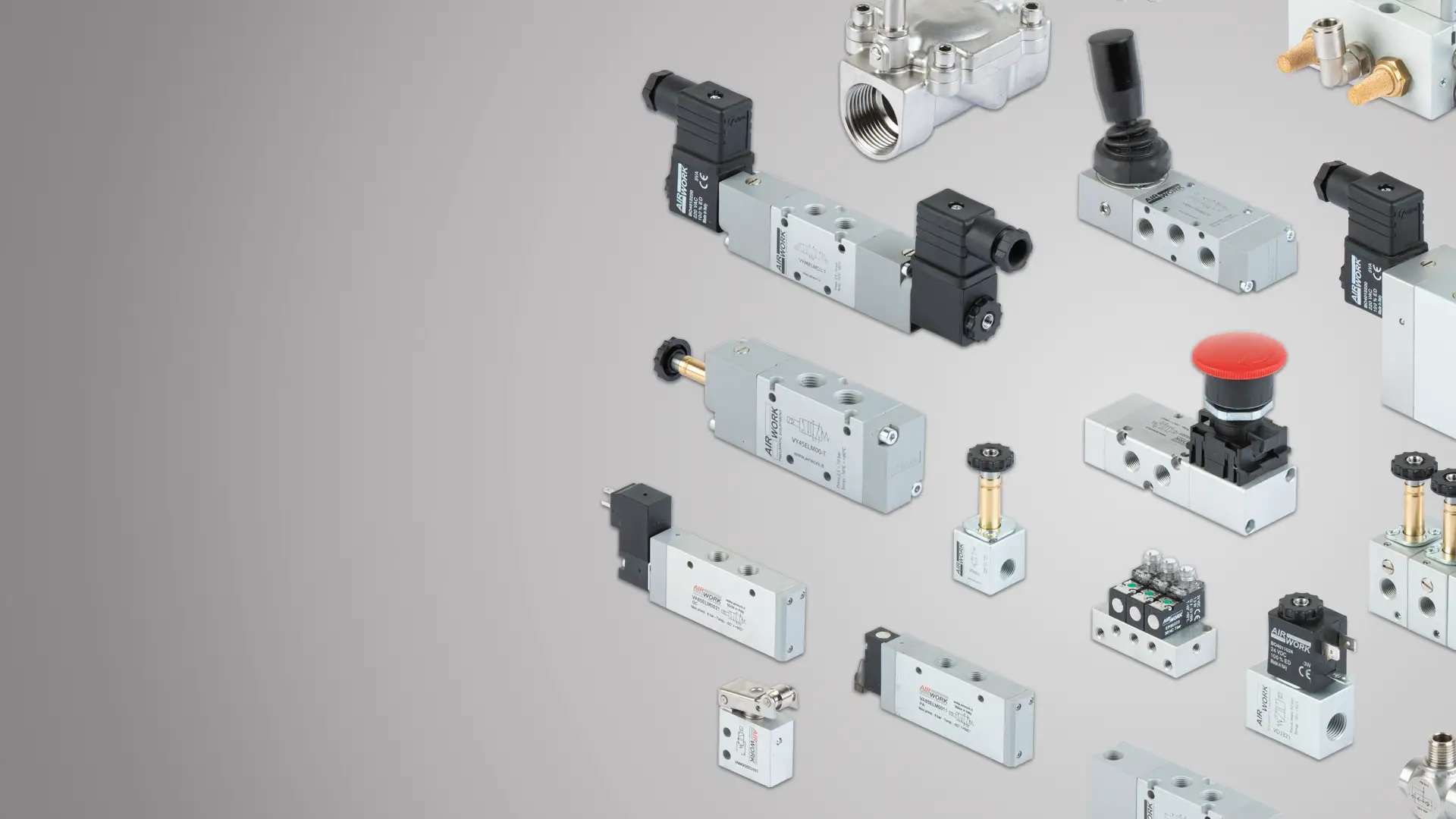
Valves and electrovalves
Search for products
Didn’t find what you were looking for?
Contact us and we will help you to find the most suitable solution
Contact usSpecial products
Customized pneumatic components for your every need
In-depth Insights into Valves and Solenoid Valves
High-quality products for excellent performance
The valve family is divided into standardized and non-standardized valve categories.
Valves manufactured according to standards include: ISO 5599/1 and Namur.
The wide range of non-standard valves includes:
- electrically actuated valves,
- pneumatically actuated valves,
- manual actuation,
- mechanical actuation,
- and a full range of auxiliary valves and air control accessories.
All valves are manufactured from aluminum alloy to ensure strength and long-term stability, a principle that Airwork (now A&T Fluid Solutions) has pursued since the very beginning of its activity.
Solenoid valves are fundamental components in industrial pneumatic systems, where they ensure precise and reliable control of compressed air flows.
These electromechanical devices make it possible to automatically control the opening and closing of pneumatic circuits, enabling the automation of complex production processes with high operational efficiency.
What is a Pneumatic Solenoid Valve, what it is used for and how it works
A pneumatic solenoid valve is a device that uses an electrical signal to control the flow of compressed air within a circuit.
The heart of the system is the solenoid, an electromagnetic actuator that, when energized, generates a magnetic field capable of moving an internal ferromagnetic core.
This mechanical movement actuates the valve sealing element, opening or closing the air passages.
The operation of solenoid valves is based on well-established electromechanical principles: when the solenoid coil is energized by electric current, a magnetic force is created that moves the internal plunger, changing the configuration of the flow paths.
Once the power supply is interrupted, in most models a return spring brings the valve back to its initial position.
This system allows for fast and repeatable switching, which is essential for applications requiring intensive duty cycles.
How many types of Pneumatic Solenoid Valves exist
In the field of industrial pneumatics, there are various solenoid valve configurations, each designed to meet specific requirements.
The choice of the correct type depends on:
- the characteristics of the circuit,
- the operating pressure,
- and the complexity of the required control.
Two-way solenoid valves represent the simplest solution, with one inlet and one outlet that allow the compressed air flow to be fully opened or closed. This configuration is ideal for on/off applications where there is no need to manage alternative flow directions.
For applications requiring greater versatility, three-way solenoid valves provide a pressure inlet, an outlet to the actuator, and an exhaust port. This architecture allows not only the supply of the pneumatic component, but also the rapid discharge of air when the valve switches, speeding up system response times.
More complex configurations include 5-way, 3-position valves, capable of controlling double-acting actuators with high precision. These solutions make it possible to manage bidirectional movements and intermediate positions, making them indispensable in advanced automation systems.
A special mention should be made of bistable solenoid valves, which maintain their position even in the absence of electrical power thanks to a magnetic latching system. These components are particularly advantageous in terms of energy savings, as they require power only during switching and not to maintain the achieved position.
For applications requiring gradual flow control, proportional solenoid valves represent the most advanced technology. These devices continuously modulate the flow rate based on the intensity of the electrical signal received, allowing precise regulation of speed and force in pneumatic actuators.
Technical characteristics and symbols
The symbols used for solenoid valves follow international standards that allow quick identification of the configuration and operation of each component.
Pneumatic diagrams use standardized graphical representations in which overlapping squares indicate the different valve positions, while lines and arrows show the flow paths.
This standardization simplifies system design and maintenance.
Solenoid valves for compressed air must meet specific technical requirements related to operating pressure, typically between 2 and 10 bar, and to the flow coefficient (Cv or Kv), which determines the ability to pass a certain volume of air.
Construction materials such as anodized aluminum for valve bodies and engineering polymers for seals ensure corrosion resistance and long operational life.
Solenoid valve connectors play a crucial role in system reliability. Modern solutions adopt connectors compliant with DIN standards or fieldbus interfaces, enabling integration with industrial control systems and facilitating remote diagnostics and parameter setting.
How to connect a Pneumatic Solenoid Valve
Proper connection of a pneumatic solenoid valve requires attention to both pneumatic and electrical aspects.
On the pneumatic side, it is essential to follow the indications for pressure inlet, actuator outlets, and exhaust ports, usually identified by standardized numbering or alphabetical coding.
The use of suitable fittings and compliance with specified tightening torques prevents air leaks that would compromise system efficiency.
From an electrical standpoint, the solenoid must be supplied with the correct voltage, typically 24V DC in modern industrial systems, although versions for 230V AC or other specific voltages are also available.
The protection of control circuits with correctly rated fuses and the installation of flyback diodes to suppress voltage spikes generated when opening the inductive circuit are essential practices to ensure longevity and reliability.
Advantages and selection criteria
The adoption of pneumatic solenoid valves in industrial environments offers numerous operational advantages.
The fast response, with switching times in the order of milliseconds, makes it possible to achieve high-speed production cycles.
Integration with electronic control systems also allows the programming of complex sequences and precise synchronization between different process stages.
Choosing the correct solenoid valve requires careful analysis of operating conditions.
For applications with standard compressed air, diaphragm valves offer a good balance between cost and performance, while high-pressure circuits require structurally reinforced solutions.
High-pressure solenoid valves, designed to operate up to 16 bar or more, incorporate materials and geometries optimized to withstand greater mechanical stresses.
In systems where steam or aggressive fluids are present, it is necessary to select specific models with seals made from materials resistant to high temperatures and corrosion.
Steam solenoid valves, for example, use PTFE seals or equivalent materials capable of maintaining integrity even at 180°C or higher temperatures.
Application sectors
Pneumatic solenoid valves are used across a wide range of industrial sectors.
In the manufacturing industry, they power pneumatic cylinders for handling, clamping, and tool actuation.
In the packaging sector, they manage dosing, labeling, and packaging systems with intensive duty cycles that require millions of switching operations without loss of performance.
The automotive industry relies heavily on these technologies for robotic assembly lines, where precise synchronization among dozens of pneumatic actuators determines process quality and productivity.
The pharmaceutical and food industries also benefit from solenoid valves made with certified materials and surface finishes that meet stringent hygiene standards.
In air treatment systems and industrial compressors, solenoid valves control regulation, bypass, and safety functions, contributing to the overall energy efficiency of the system.
The ability to integrate position sensors and feedback systems also enables the implementation of predictive control logic that optimizes consumption and prevents unplanned downtime.
Continuous technological evolution has led to the development of increasingly compact and efficient solenoids, with reduced power consumption and integrated diagnostic capabilities, confirming these components as indispensable elements in modern pneumatic automation.
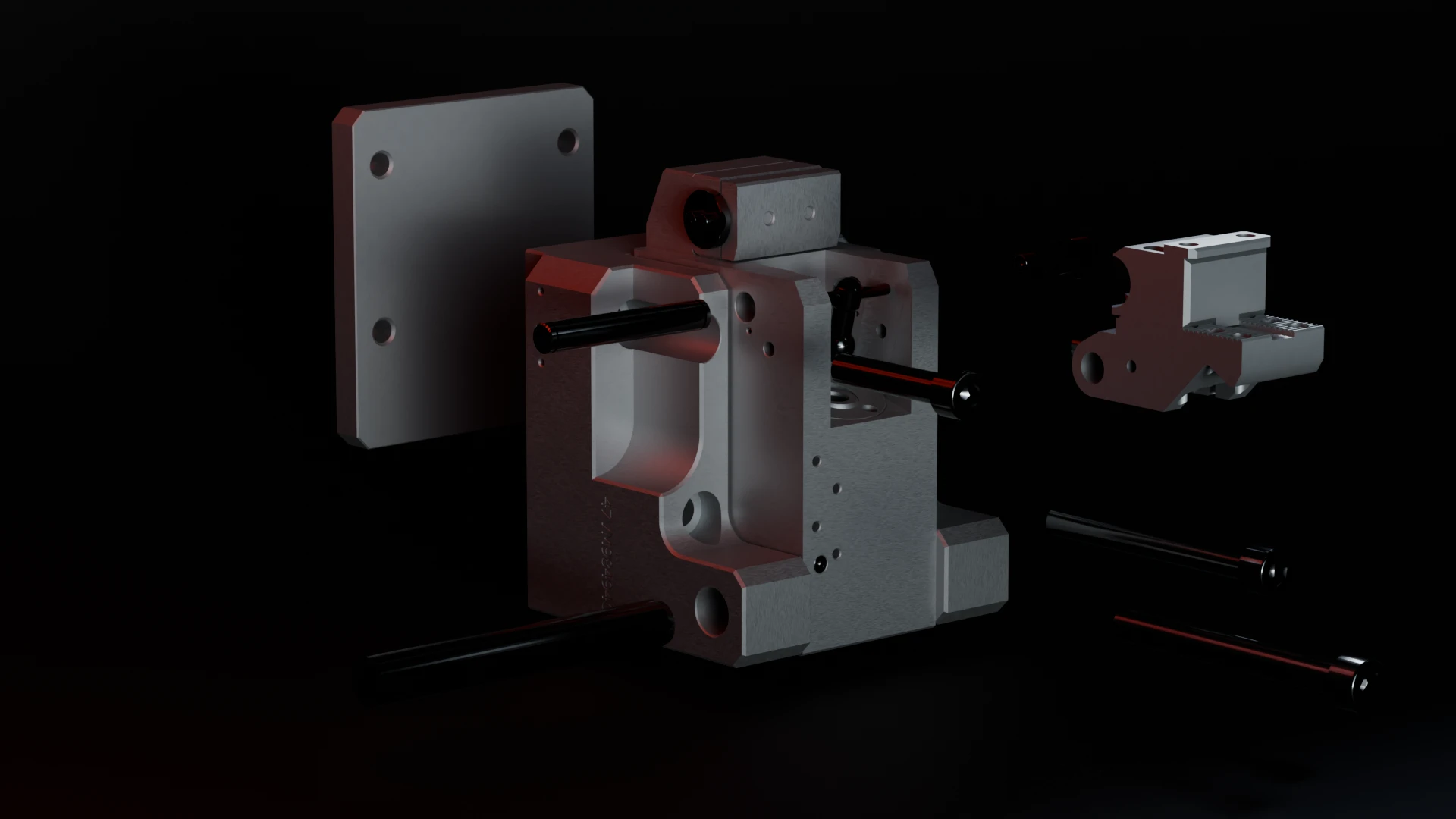
Special products
tailor-made
A&T stands out for its ability to offer custom-made products, designed to meet every specific need in the field of pneumatic and hydraulic solutions. We guarantee precision, quality, and innovation in every detail to ensure maximum efficiency and reliability.